Which best explains the following trend. Which best explains the following trend.
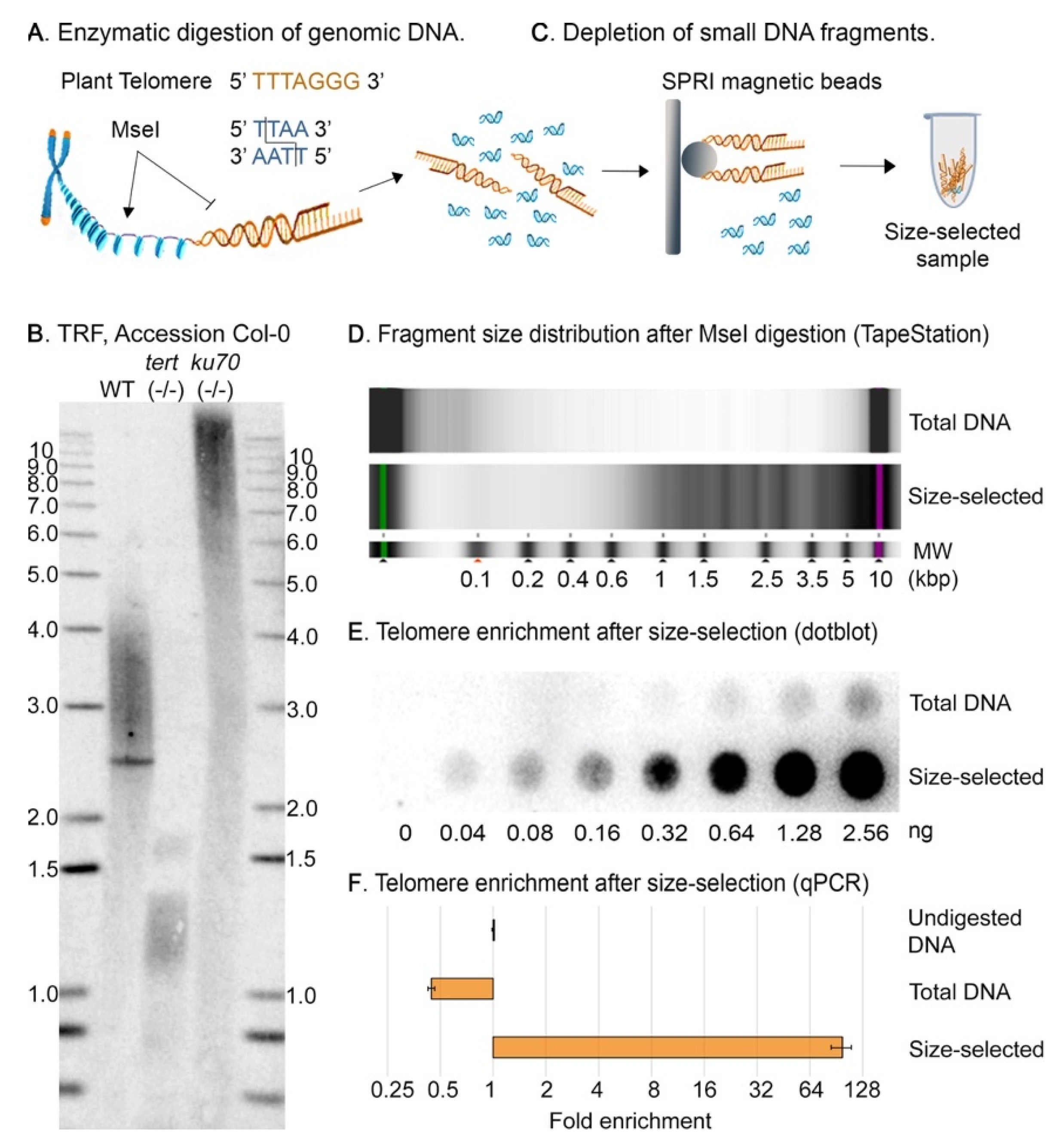
Ijms Free Full Text Quantification Of 8 Oxog In Plant Telomeres Html
K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 Xe 170 a.
. 100 C 373 K. SbH 3 17C AsH 3 55C PH 3 87C NH 3 33C The first three compounds illustrate a trend where the boiling point decreases as the mass decreases. Which best explains the following trend.
However one can determine the valency of an element simply from its position in the. In the Voigt configuration the two elements are connected in parallel and both elements are subjected to the same strain but different stress. Atomic size measured the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the outermost non-valence electrons of the atom.
C K 273 eg. The basic equation for strain rate in the Maxwell model is. A Carbon C b Silicon Si c Boron B d Fluorine F 3.
At the same time electrons are added to the atoms as you move from left to right across a period. Element bp K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 Xe 170. As you move from left to right the nucleus gains protons.
σtot σD σS. Unique Chemistry of the Lightest Elements. As you move from left to right across a period the physical properties of the elements change.
Explain the trends you observed for bromine chlorine magnesium sodium and phosphorus. These inner 3d electrons offer a poor shielding effect and thus valence shell electrons of Ga experience greater nuclear attraction. Using orbital energy arguments explain why electron configurations with more than four electron pairs around the central atom are not observed for second-period elements.
Which best explains the following trend. One loose trend is the tendency for elemental states to go from solid to liquid to gas across a period. See the answer See the answer done loading.
Based on the data given in part a the radius of the ion Zn2 is expected to be closest to that of which group 2A element. Which essentially implies breaking a few bonds. Hydrogen bonding O DLe Chateliers principle E none of these.
Because of equal strain in both elememts the model is also known as. Hydrogen bonds account with for which of the following observation. What intermolecular forces isare present in solid SO3.
Identify the element in a 2nd period and 14th group with valency 4. In the extreme cases Groups 1 and 18 we see that Group-1 elements are all solids and Group-18 elements are all gases. Li Be B C N O and F differs in many important respects from that of the heavier members or congeners of the groupConsequently the elements of the third period n 3.
Atomic size decreases from. Explain the trends in the following properties with reference to group 16. Chemistry nya 4 A15 6 The elements of group 5A the nitrogen family form compounds with hydrogen having the boiling points listed below.
Chemistry questions and answers. These electrons reside in the same energy shell and do not offer complete shielding. Which compound listed below has hydrogen bonding.
Who are the experts. London dispersion forces b. However there is an anomaly observed in the atomic radius of gallium due to the presence of 3d electrons.
The temperatures are given in kelvin K. As you already know the valency of an atom is the number of electrons it has in its outermost shell or the number of atoms in requires to complete its outermost shell. The graph shows how melting points and boiling points vary across period 3.
In group 13 on moving down the group the atomic radii increases from B to Al. D ε d t 1 E d σ d t σ η. Explain whether they matched the predicted periodic trends.
Electronic configuration of an element x is 281 and for Y 287 then mention the bond existing between 2 elements. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the. You can easily convert K to C and back again.
Chemistry questions and answers. Which best explains the following trend. Element BP K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 170 O A London dispersion forces OB Dipole-Dipole Interaction C.
Le Chateliers principle E none of these Xe Question 15 Steel is an A interstitial alloy O Bionic. Describe and explain the trends in melting and boiling points across period 3. One of the trends in the modern periodic table is that of the valency of an atom.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. This problem has been solved. Calulate the quantity of electricity required in coulomb.
Trends are based on Coulombs law which mathematically relates several characteristics of an elements. For its molar mass water has a high boiling point. This increases the positive charge of the nucleus and its attractive force on the electrons.
The melting point of an element is basically the energy required to change the state of an element from its solid state to its liquid state. A Covalent bond b Ionic bond c Hydrogen bond d Metallic bond 2. However ammonia NH 3 does not follow the.
K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 Xe 170 O A. 1 Atomic radii and ionic radii. Which best explains the following trend.
Let us look at the elements in the ascending. Which of the following solutions will be the best buffer at a pH of 926. Le Chateliers principle E.
In the electolysis of AgNO 3 solution 07g of Ag is deposited after a certain period of time. Na Mg Al Si P S and Cl are generally more representative of the group to which they belong. Le Chateliers principle e.
The chemistry of the second-period element of each group n 2. Periodic trends predict differences between elemental characteristics as you move across the periodic table. The ionic radii decreased across a period for the positive sodium and magnesium ions.
Ka for HC2H3O2 is 18 x10-5 Kb for NH3 is 18x10-5. K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 Xe 170. 1London dispersion 2dipole-dipole 3hydrogen bonding 1 only.
B The lattice energy of ZnH2 is 2870kJmol. The given elements belong to group 18. Thus higher the stronger the bond between the atoms higher will be the melting point.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards terms like Among the elements of the main group the general trend in the first ionization energy moving across a period is not followed between group 2 and group 13. Which best explains the following trend. London dispersion forces O B.
The atomic radii decreased across Period 3 and increased down Group 17. K He Ne 4 25. Dipole-Dipole interaction O C.
K He 4 Ne 25 Ar 95 Kr 125 Xe 170 O A. K He-4 Ne-25 Ar-95 Kr-125 Xe-170 A. CaH2 2410 kJmol SrH2 2250kJmol.
View the full answer. Al 418 kJmol Si 1341 kJmol P 720 kJmol and S 2004 kJmol. Order the intermolecular forces dipole-dipole London dispersion ionic and hydrogen bonding from weakest to strongest.
K He Ne 4 25 95 125 170 Ar Kr A London dispersion forces B dipole-dipole interaction C hydrogen bonding D Le Chateliers principle E none of these. Explain the following trend in electron affinities. There is a lot going on in this.
Which best explains these exceptions Which element has the largest atomic radius Which is a correct set of values of m for one of the subshells of n 2. Which best explains the following trend. A Explain the following trend in lattice energy.
Q1 correct answer is option A. Which best explains the following trend.

Minerals Free Full Text Physicochemical Characterization Of Natural Wollastonite And Calcite Html

Gold Crystal Pendentif Light Hanging Lighting Fixture Home Etsy Crystal Pendant Lighting Modern Chandelier Hanging Lights
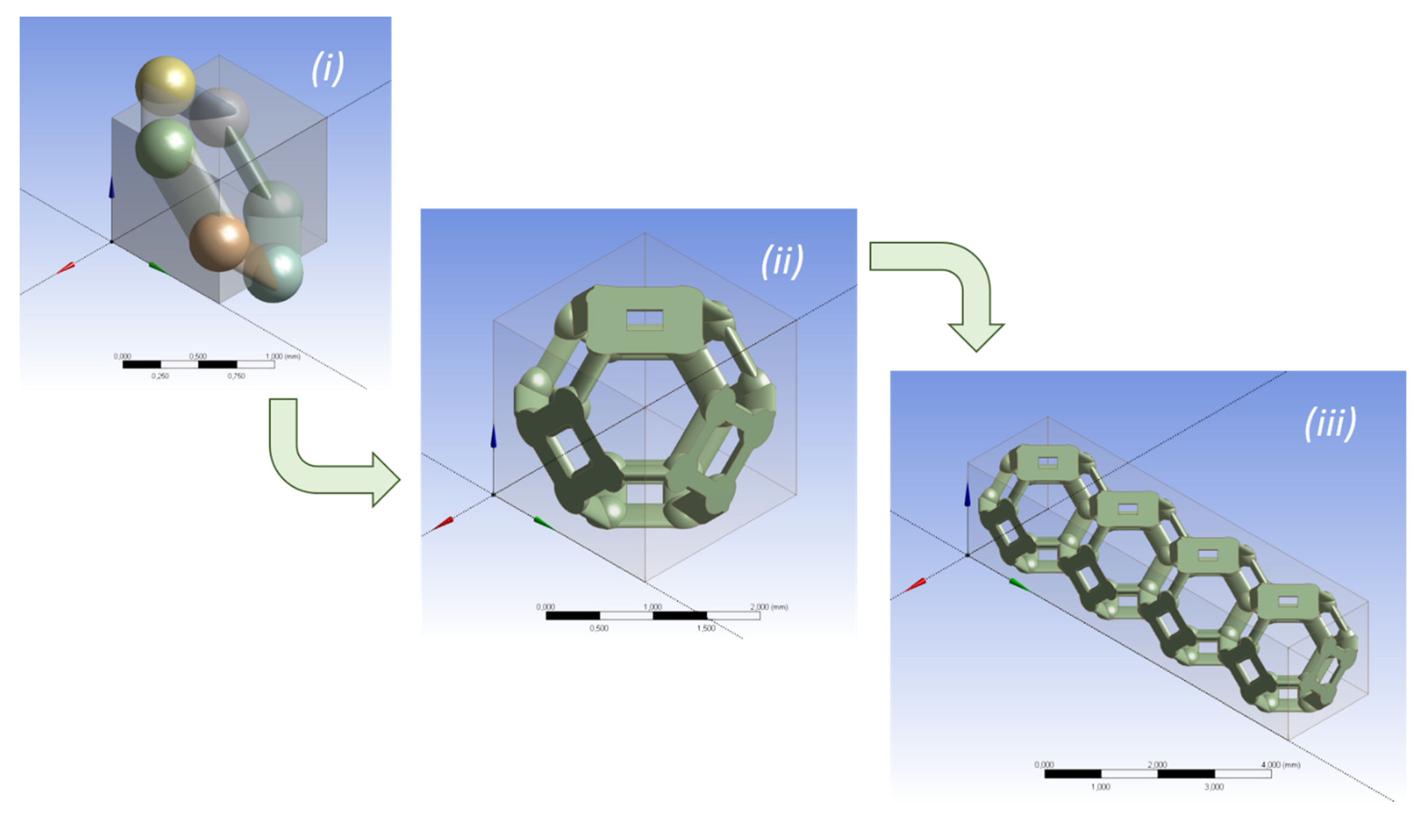
Applied Sciences Free Full Text Numerical Analysis Of The Effects Of The Structure Shape And Orientation Of Kelvin Cell Porous Structures During Air Forced Convection Html

Elucidating The Atomic Structures Of The Gel Layer Formed During Aluminoborosilicate Glass Dissolution An Integrated Experimental And Simulation Study The Journal Of Physical Chemistry C
0 Comments